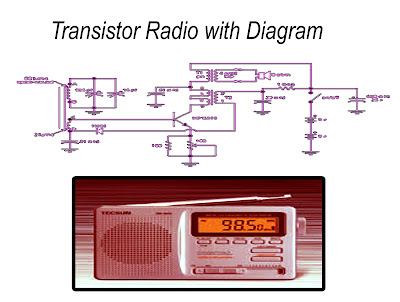
Transmitters, generating high-frequency electromagnetic waves to be sent by way of the energy transmitted by the antenna are electronic devices. They are made in a variety of types according to their use of power and purpose. The main task of the transmitting antenna to provide power at a certain frequency, and to transmit information with the help of electromagnetic waves generated in this way. First time donors only could send high-frequency energy at a fixed frequency. Such transmitting continuous wave (CW Continuous wave) is called transmitters. With these information transmission is only possible in coded (such as Morse code)
Recently requested information (especially speech, music and video) of a carrier wave (Carrier Wave) is sent superimposed. This process is called modulation and such waves modulated continuous wave. MCW (Continious Wave Modulated) transmitter are divided into two main categories according to the modulation method.
1. Amplitude (Amplitude) modulated transmitters:
Double yanbantl full-makers carrier (DSB-Double side band).
Double-sideband suppressed carrier (DSB-SC = Double Side Band - Supressed Carrier)
2 Yanbantl single transmitter (SSB-Single Side Band)
Single-sideband suppressed carrier (SSB-SC = Single Side Band - Supressed Carrier)
Angle-modulated transmitters:
Frequency modulation transmitters (FM-freguency Modulation).
Phase modulation transmitters (AM-phase modulation).
Generally, three types of transmitters used in practice. These are:
AM transmitters.
FM transmitters.
SSB transmitters.
The simplest one AM transmitter consists of four main sections.
Oscillators solid.
Solid buffer (Buffer).
High Frequency (RF) power amplifier.
Modulator floor (this floor is not available in the CW transmitter).
Oscillator: This is the most important part of the transmitter. Radio Frequency (greater than 100 kHz) produces energy. The frequency of the energy generated must remain within certain limits here. Otherwise it cannot be monitored.
Modulator and audio frequency stage: the electrical signal obtained from the microphone is too small. Audio-frequency amplifier (solid) raises its desired level. The modulator is also an adaptive layer that transmits sound signals to the power stage. The power stage according to the intensity of the sound by influencing the frequency amplitude gain (amplitude) performs modulation.
A simple FM transmitter consists of the following layers:
Audio frequency amplifier and reactance modulator solid. (Reactance: Coil or alternating current resistance of the capacitor.)
Oscillators solid.
Solid bumper and the driver.
RF power amplifier solid.
Solid buffer (Buffer): Buffer solid, solid insulates power from the oscillator. Thus oscillator provides more stable work. If desired this layer may also remove two or three times the frequency of the oscillator, the frequency multiplier is called.
RF power level: This layer feeds in the desired signal power to the antenna; information from a modulator is superimposed on a carrier wherein the oscillator
The audio frequency amplifier and the reactance modulator: the signal from the microphone is applied to the reactance modulator raised to the desired level. Reactance modulator, the oscillator circuit capacitive or inductive reactance of the coil or remove it added. Thus, according to the intensity of sound frequencies by changing the oscillator frequency FM (Frequency Modulation) is provided.
Oscillator: generates radio-frequency energy within certain limits. (As standard FM radio channel is from the 85-108 MHz)
Buffer and driver: wherein the replication process is performed if both the frequency and the desired sealing action.
RF power amplifier: Frequency modulated signals from the antenna until the level rises will spread on the floor.